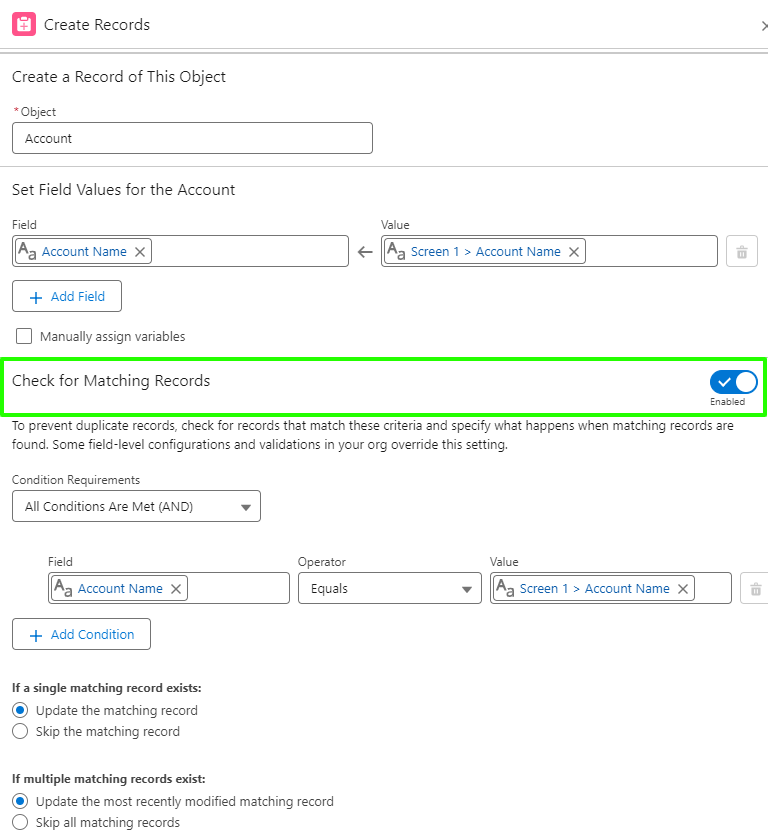
In managing ongoing Business As Usual (BAU) requests, one particular ticket stood out: “Automating Logistics Contact Updates for Opportunities” The goal was to streamline how logistics contacts are handled in opportunities involving event-related products, ensuring a smooth and consistent contact assignment across all opportunity products. Here’s a breakdown of the requirements, the solution components implemented, and the benefits this automation brought to the process.
Requirements Breakdown
- Single Logistics Contact Per Opportunity
Each opportunity should have a unique Logistics Contact to avoid duplicate contacts. This required a validation rule to prevent more than one contact with the “Logistics” role from being added. - Automated Contact Population for Opportunity Products
When a Logistics Contact is assigned at the opportunity level, it should automatically populate all associated opportunity products, ensuring consistency. - Flexible Contact Management for Each Product Line
Users need the flexibility to replace the Logistics Contact on individual opportunity products, allowing them to specify different logistics contacts where needed. - Selective Contact Updates Based on Opportunity Status
Updates to the Logistics Contact at the opportunity level should only affect products with a future service date, preserving historical accuracy for past events. - Automatic Contact Assignment for New Products
Newly added products should inherit the existing Logistics Contact, ensuring continuity as opportunities evolve. - Exclusion of Manually Updated Contacts from Future Automation
Products with manually updated Logistics Contacts should not be overwritten by future updates, maintaining user control over specific contacts.
1. Create a Lookup Field for Logistics Contact on Opportunity Product
- Field: Logistic_Contact_Name__c
- Purpose: Holds the designated Logistics Contact for each opportunity product.
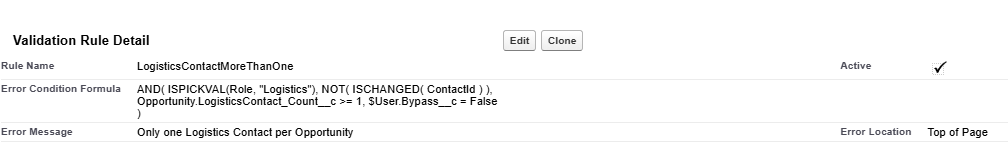
2. Set Up a Validation Rule
- Rule: “Only One Logistic Contact Per Opportunity”
- Purpose: Ensures only one contact with the role of “Logistics” can be assigned to each opportunity, preventing duplicate contacts.
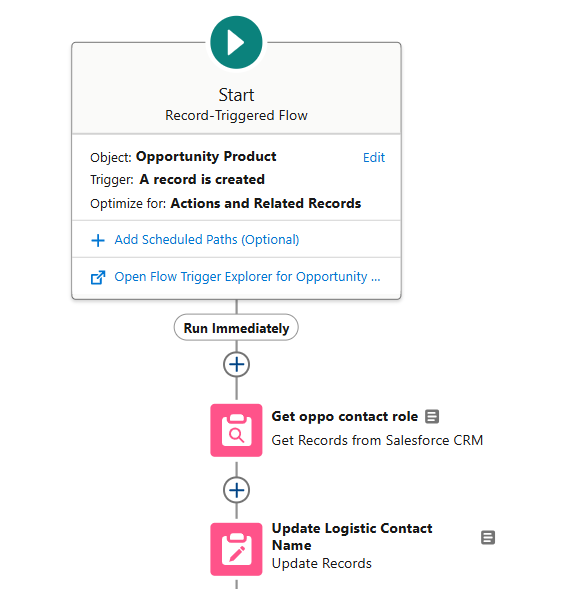
3. Create the Update Opportunity Contact Role Flow
- Trigger: Activates when an Opportunity Contact Role with “Logistics” is created or updated.
- Conditions: Role Equals Logistic
- Decision: Check if the record is new or if the Logistics Contact ID has changed.
- Outcome: ISNew: Updates the Logistic_Contact_Name__c field on all opportunity products with the current Logistics Contact.
Is changed: Updates the Logistic_Contact_Name__c field on the future service End date opportunity products with the current Logistics Contact.
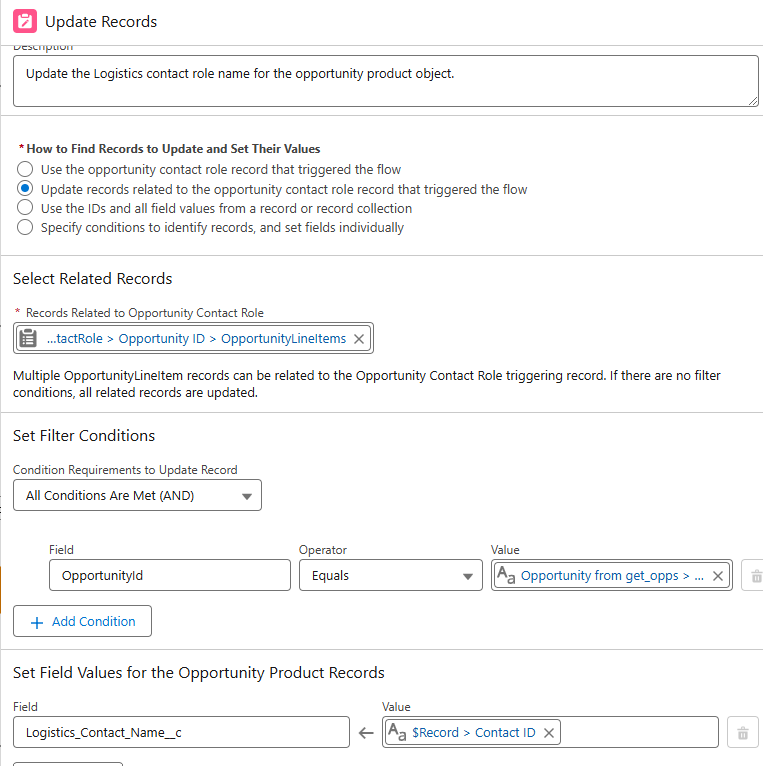
4. Create the Delete Opportunity Contact Role Flow
- Trigger: Activates when a contact role with “Logistics” is removed from the opportunity.
Outcome: Clears the Logistic_Contact_Name__c field from associated opportunity products.
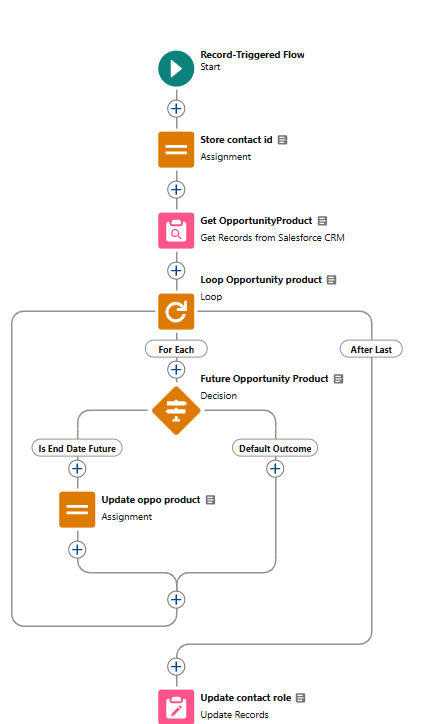
5. Create the New Opportunity Product Flow
- Trigger: Runs whenever an opportunity product is created.
- Outcome: If a Logistics Contact already exists on the opportunity, this flow populates it in the Logistic_Contact_Name__c field on the new product.
Solution in Action
With this setup, the process was able to:
- Automate Logistics Contact population across opportunity products,
- Allow manual overrides where needed,
- Ensure updates apply only to relevant products based on service dates,
- And maintain data integrity by excluding manually adjusted contacts from automated updates.
Benefits and Reflections
The implementation of this solution for the BAU ticket “Automating Logistics Contact Updates for Opportunities” enhanced the efficiency, accuracy, and flexibility of logistics contact handling. It also provided a robust foundation for managing logistics contacts on future event opportunities, saving significant time and manual work for the team.